Subscribe to Aircraft collections by Email
Ø The
Lockheed SR-71 "Blackbird" is a long-range, Mach 3+ strategic
reconnaissance aircraft that was operated by the United States Air Force.
Ø It was developed as a black project from the
Lockheed A-12 reconnaissance aircraft in the 1960s by Lockheed and its Skunk
Works division.
Ø The
SR-71 has been given several nicknames, including Blackbird and Habu.
Ø It
has held the world record for the fastest air-breathing manned aircraft since
1976; this record was previously held by the related Lockheed YF-12.
The Mighty J58 - The SR-71's Turbo-Ramjet Engine
|
Role
|
Strategic
reconnaissance aircraft
|
|
National origin
|
United
States
|
|
Manufacturer
|
Lockheed,
Skunk Works division
|
|
Designer
|
Clarence
"Kelly" Johnson
|
|
First flight
|
22
December 1964
|
|
Introduction
|
1966
|
|
Retired
|
1998
(USAF), 1999 (NASA)
|
|
Status
|
Retired
|
|
Primary users
|
United
States Air Force, NASA
|
|
Number built
|
32
|
|
Unit cost
|
$34
million
|
|
Developed from
|
Lockheed
A-12
|
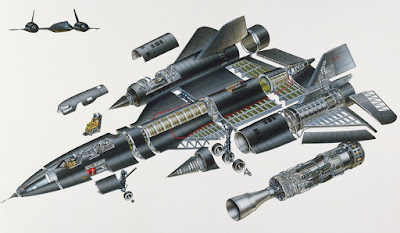
General characteristics
Ø Crew:
2: Pilot and Reconnaissance Systems Officer (RSO)
Ø Payload:
3,500 lb (1,600 kg)
Ø Length:
107 ft 5 in (32.74 m)
Ø Wingspan:
55 ft 7 in (16.94 m)
Ø Height:
18 ft 6 in (5.64 m)
Ø Wing
area: 1,800 ft2 (170 m2)
Ø Empty
weight: 67,500 lb (30,600 kg)
Ø Loaded
weight: 152,000 lb (69,000 kg)
Ø Max.
takeoff weight: 172,000 lb (78,000 kg)
Ø Wheel
track: 16 ft 8 in (5.08 m)
Ø Wheelbase:
37 ft 10 in (11.53 m)
Ø Aspect
ratio: 1.7
Ø Powerplant:
2 × Pratt & Whitney J58-1 continuous-bleed afterburning turbojets, 34,000
lbf (151 kN) each
Performance
Ø Maximum
speed: Mach 3.3 (2,200+ mph, 3,540+ km/h, 1,910+ knots) at 80,000 ft (24,000 m)
Ø Range:
2,900 nmi (5,400 km)
Ø Ferry
range: 3,200 nmi (5,925 km)
Ø Service
ceiling: 85,000 ft (25,900 m)
Ø Rate
of climb: 11820 ft/m (60 m/s)
Ø Wing
loading: 84 lb/ft² (410 kg/m²)
Ø Thrust/weight:
0.44